Solid-state white light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are next-generation lighting devices for replacing the traditional incandescent and fluorescent lamps due to their superior properties such as energy-saving, robust, long-lifetime and environment-friendly features. Nowadays, a blue diode chip combined with Y3Al5O12:Ce3+ (YAG:Ce3+) yellow phosphor is the most mature method for fabricating commercial white LEDs.
Because of the lack of red light component in the emission of YAG:Ce3+, it is notoriously difficult to make warm white LEDs with high color rendering index (CRI, Ra >80) and low correlated color temperature (CCT <4500 K), both of which are key requirements for some important applications such as indoor lighting. This difficulty can be overcome by adding a suitable red phosphor in LEDs to complement the red light component. To this end, great efforts have been made to exploit novel rare-earth doped red phosphors, and the most successful materials are Eu2+ or Ce3+ doped (oxy)nitride compounds.
However, these (oxy)nitride red phosphors are limited by their high cost and low luminous efficacy due to the rigorous synthesis conditions and ultrabroad emission band, respectively. Therefore, an ideal red phosphor with relatively narrow absorption and emission bands, a high PL QY and low production cost is highly desired for warm white LEDs.
Recently, in a collaboration, Prof. CHEN Xueyuan’s group of Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. LIU Rushi’s group of National Taiwan University have developed a novel cation exchange method for synthesizing Mn4+ ions activated fluoride red phosphors including K2TiF6:Mn4+, K2SiF6:Mn4+, NaYF4:Mn4+ and NaGdF4:Mn4+ (Nat. Commun.2014,5, 4312).
These phosphors exhibit the most intense excitation band at ~460 nm with a bandwidth of ~50 nm, which is perfect for blue-chip excitation. The sharp red emissions are centered at ~630 nm, thereby rendering a higher LER in warm white LEDs as compared to (oxy)nitride red phosphors that show substantial emission spreading into deep red spectral region.
Particularly, the photoluminescence (PL) quantum yield for K2TiF6:Mn4+ red phosphor is as high as 98%. This phosphor also shows good thermal stability, i. e., the PL intensity at 150 °C remains 98% of that at room temperature. By integrating this phosphor with commercial YAG:Ce3+ yellow phosphor and 455-nm blue chip, the researchers have fabricated a warm white LED with high CRI (Ra = 81), low CCT (3556 K) and a record-high luminous efficiency of 116 lm W-1 under rated 60-mA drive current.
By means of low-temperature high-resolution spectroscopy, the detailed electronic/vibronic structure of Mn4+ ions in K2TiF6 host has been elaborated. Based on PL dynamics, PL QY and theoretical analysis, they also reveal the mechanism for abnormal dependence of PL intensity on the temperature in K2TiF6:Mn4+. These findings show great promise of K2TiF6:Mn4+ as a commercial red phosphor in warm white LEDs, and open up new avenues for the exploration of novel non-rare-earth red emitting phosphors.
This research is supported by the Special Project of National Major Scientific Equipment Development of China (No. 2012YQ120060), the 973 program of MOST (No. 2014CB845605), the NSFC (No. 11004191, U1305244 and 21325104), the Key Project of Science and Technology Foundation of Fujian Province (Nos. 2011HZ0001-2 and 2013I0009), and the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (Contract No. MOST 101-2113-M-002-014-MY3).
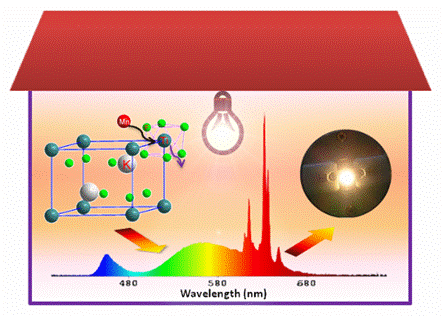
K2TiF4:Mn4+ red phosphor synthesized through cation exchange and highly efficient warm white LEDs based on this phosphor