Biaryls and heterobiaryls are ubiquitous structure scaffolds in natural products, pharmaceuticals, and organic functional materials. As a result, developing direct and convenient methods that employ readily available and easy-to-handle starting materials to construct bi(hetero)aryls with regioselectivity attracts immense attention of chemists.
Supported by the 973 Program, NSFC and Key Project from CAS, Prof. SU Weiping and his colleagues from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed transition-metal catalyzed decarboxylative C-H arylation reactions.
The radical decarboxylative C-H alkylation of (hetero)arenes known as the Minisci reaction was named after its discoverer F. Minisci in the late 1960s and has been widely utilized to construct C-C bond since its discovery. This reaction is particularly important and provides an access to functionalization of hetero aromatic cycles especially electron-deficient ones which were inert towards Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction with new reactivity and selectivity, thus represented an important breakthrough in the history of organic chemistry.
Nevertheless, one drawback of the Minisci reaction is the limitation of nucleophilic radicals, especially of the aryl variety. Recently The researchers led by Prof. Su successfully extend this chemistry to aryl nucleophilic radicals by using inexpensive silver catalyst and abundant carboxylic acids as arylating reagent (Figure 1). The reported reaction also showed good functional group compatibility, and provided an atom-economical and efficient route for biaryl synthesis. The study has been published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2199.

Figure 1: Silver-catalyzed decarboxylative C-H bond arylation of (hetero)arenes(Image by Prof. SU)
Developing transition-metal-catalyzed functional-group-directed C-H functionalization reactions is one of the core research fields in organic chemistry and provides a direct access to functionalization of organic molecules. However, the installation and removal of the directing group remains problematic when they are undesired to the target molecules. To solve this problem the concept of traceless directing strategies has been proposed.
Inspired by their previous work on ispo-decarboxylative C-H arylation of thiophenes, Prof. SU’s group successfully applied the traceless concept to our ortho-decarboxylative C-H bond arylation of heterocycles by taking the advantage of the dual roles in which aryl carboxylic acids could serve namely as arylation reagent and traceless directing group (Figure 2).
This reaction is compatible with diverse substitution patterns on the aryl ring of the benzoic acid and a broad range of functional groups, and is applicable to synthesis of a biologically active compound that is hard to access through conventional synthetic routes. The study has been published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3817.
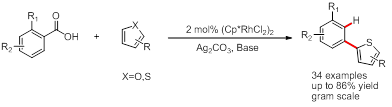
Figure 2: Rhdium-catalyzed ortho-decarboxylative C-H bond arylation of heterocycles(Image by Prof. SU)
Contact:
Prof. SU Weiping
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
No.155 Yangqiao West Road, Fuzhou, Fujian 350002, China
E-mail: wpsu@fjirsm.ac.cn