Metal-organic clusters (MOCs) exhibit a number of interesting physical properties. However, their fairly small specific surface area prohibits straightforward applications in heterogeneous catalysis, homochiral synthesis, and enantiomer separation. To overcome this limitation of applications, loading MOCs into porous host metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) is a great challenge but very interesting for preparation of composite materials.
Recently, Double Zhang Team of Synthetic Inorganic Chemistry led by Prof. ZHANG Jian and Prof. ZHANG Lei at the State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, cooperated by Prof. Christof Wöll’s group in Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, has successfully prepared the nanoclusters@MOF thin film applying a modified liquid-phase epitaxial (LPE) approach.
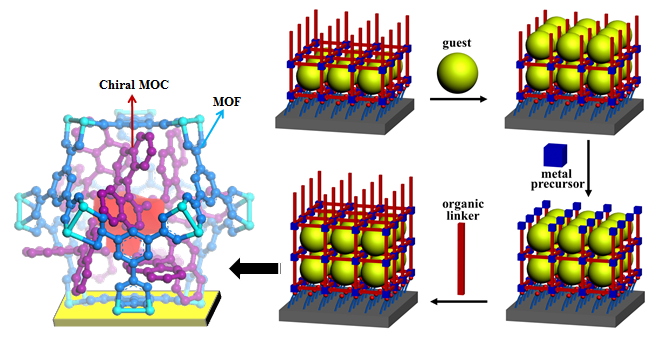
Schematic presentation of layer-by-layer growth of Ti-MOC–loaded HKUST-1 thin film(Image by Prof. ZHANG’s group)
The results reveal that the applied LPE-based loading procedure can yield a well-defined, 3D MOCs array. And the distribution of MOCs in the film is complete and homogeneous. The optical activity of the chiral Ti-MOC and metacrystals allows the use of CD spectroscopy to demonstrate a first application: efficient enantiomer separation for methyl lectate. The method introduced here can also be applied to other MOFs and – with regards to the fabrication of metacrystals - allows definition of the periodicity of the target NP lattice, providing sufficient, tailorable porosity.
This approach is also suitable for producing metacrystals from other subunits, such as nonspherical NPs. Additionally, they have also encapsulate Lanthanide Coordination Compounds NPs into MOF thin film using the same approach to provide applications in LED sensor.
This research was supported by the 973 program (2012CB821705) and NSFC (21425102, 21501176 and 21221001). The studies entitled " Chiral Porous Metacrystals: Employing Liquid-Phase Epitaxy to Assemble Enantiopure Metal–Organic Nanoclusters into Molecular Framework Pores" and “Liquid-Phase Epitaxy Effective Encapsulation of Lanthanide Coordination Compounds into MOF Film with Homogeneous and Tunable White-Light Emission” have been published in ACS Nano and ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, details could be found at 10.1021/acsnano.5b06230 http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsnano.5b06230 and 10.1021/acsami.5b09975 http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.5b09975.