Nuclear energy and the nuclear fuel cycle mandate strict the management and safeguards that require the removal and recovery of hazardous radionuclides from nuclear waste. Uranium is one of the radioactive elements in nuclear wastes. U(VI) dissolves in water as the uranyl cation UO22+ with significant mobility, which can easily enter into the food chain with serious health effects.
On the other hand, the ocean contains 4.5 billion tons of uranium (at about 3.3 ppb) thus it is a potential huge resource of uranium that may supply uranium for nuclear energy for several thousand years. Thus, it is strategically and ecologically important to capture the uranium(VI) from aqueous solutions for further treatment, disposal and utilization.
Dr. FENG Meiling from Prof. HUANG Xiaoying’s research group in Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, cooperates closely with Prof. Mercouri G. Kanatzidis from Northwestern University, USA. Recently they reported the first example of chalcogenido ion-exchanger, namely [Me2NH2]4/3[Me3NH]2/3Sn3S7·1.25H2O (FJSM-SnS), in which the organic amine cations can be selectively exchanged by the UO22+ ions.
FJSM-SnS’s outstanding features include: i) High exchange capacity. The maximum uranium exchange capacity of FJSM-SnS is 338 mg/g, comparable to those of the best reported uranium adsorbents and much more than those of the commercial UO22+-scavenger. ii) Excellent super acid and alkali resistance. It could keep the framework robust over a broad pH range (2.1 ― 11) upon ion-exchange process. iii) High selectivity. It could efficiently capture the UO22+ ions in the presence of the high concentrations of Na+, Ca2+ or HCO3- (the highest Kd value reached 4.28 × 104 mL/g). iv) Regeneration.
The material could be easily regenerated with a cost-affordable and environmentally friendly method, i.e. by treating the UO22+-laden materials with a concentrated KCl solution.
These advantages coupled with low cost, environmentally friendly nature and facile synthesis make FJSM-SnS a new promising remediation material of radioactive U removal and recovery from nuclear waste solutions.
These results entitled " Efficient Removal and Recovery of Uranium by a Layered Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Thiostannate" have been published in J. Am. Chem. Soc..
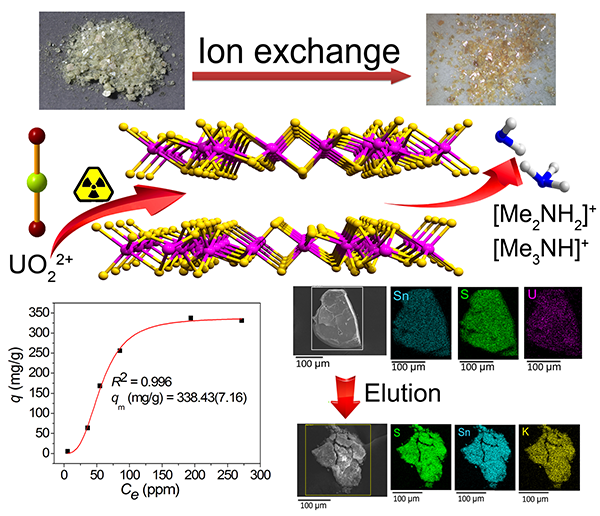
UO22+ ion-exchange of FJSM-SnS (Image by Prof. HUANG’s Group)
Contact:
Prof. HUANG Xiaoying
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: xyhuang@fjirsm.ac.cn