Organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) have attracted great attention in the past three decades for their tremendous application potential in new-generation lighting and displaying. While great progress has been made, one challenge that is how to develop stable and efficient blue OLED emitters and devices still remains.
In a study published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., the research team led by Prof. LU Canzhong from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter of Chinese Academy of Sciences reported two newly designed and synthesized highly efficient blue thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) materials (B-oCz and B-oTC).
They found that in these molecules, charge is transferred through the aryl linker and through space simultaneously due to the significant intramolecular D-A interaction. The combined charge-transfer pathway allows very small DEST and enough large transition dipole moment at the same time. Besides, they showed that the strong intramolecular interactions could effectively suppress intramolecular vibration relaxation which accelerates radiationless decay.
It is particularly interesting that the concentration quenching can be effectively inhibited in films of these compounds. They show high photoluminescent quantum yields of 0.61 (for B-oCz) and 0.94 (for B-oTC) even in neat films.
These materials were found to exhibit high chemical and thermal stability, and excellent solution processability. The blue non-doped organic light emitting diodes based on B-oTC prepared from solution processes shows record-high EQE of 19.1%. The combined charge-transfer pathway may represent a very promising new strategy for developing novel and efficient TADF materials.
This team has also developed highly efficient luminescent materials based on Cu(I) and Ag(I) complexes, and the results were published in Chem. Mater., J. Mater. Chem. C, Chem. Commun., J. Mater. Chem. C.
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Key Program of Frontier Science, CAS, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province.
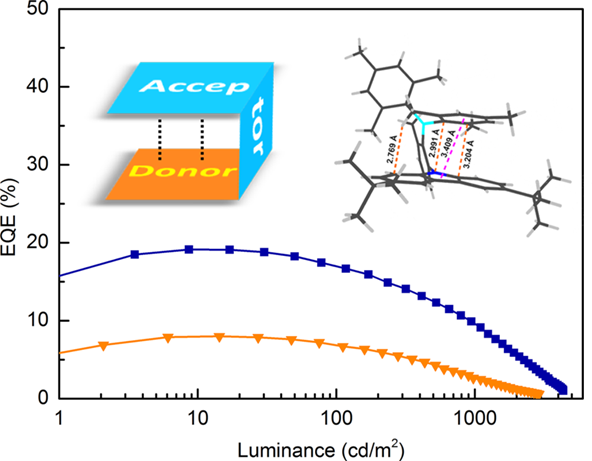
Plots of external quantum efficiency versus luminance of the non-doped devices; left inset: configuration of the investigated compounds; right inset: crystal structure and selected intramolecular distances of B-oTC. (Image by Prof. LU's Group)
Contact:
Prof. LU Canzhong
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: czlu@fjirsm.ac.cn