Mn4+ ions doped fluoride phosphors have attracted increasing attention because of their strong absorption at blue light region, high emission efficiency, and sharp line emissions at ~ 630 nm (FWHW < 7 nm),thus showing great potentiality in the field of wide-gamut displays. However, these fluoride phosphors suffer from their poor stability in moisture environment.
In a study published Angew. Chem. In. Ed., the research group led by Prof. ZHU Haomiao and Prof. CHEN Xueyuan from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter (FJIRSM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported a convenient reverse cation exchange method for preparing core-shell structured K2TiF6:Mn4+@K2TiF6 phosphor with high emisison efficiency and excelllent moisture-resistant performance.
The outer inert K2TiF6 shell can not only act as a shield for preventing moisture in the air to hydrolyze inner MnF62- group, but also effectively cut off the path of energy migration to surface defects, thus increasing the emission efficiency, especially for the phosphors doped with high Mn4+ concentration.
As a result, for the 7 at.% doped sample, the photoluminescence quantum yield increased from 75% to 93%.
By employing this sample as red phosphor, the packaged white LED exhibited an extraordinarily high luminous efficacy of 162 lm W-1, a CCT of 3510 K and a color rendering index of 93 (Ra) at the drive current of 60 mA.
Particularly, the aging tests performed on this device at 85 oC and 85% humidity for 480 h show that the luminous efficacy retains as high as 89% with respect to its initial value.
This study provides new strategy for the design and synthesis of moisture-resistant fluoride red phosphors.
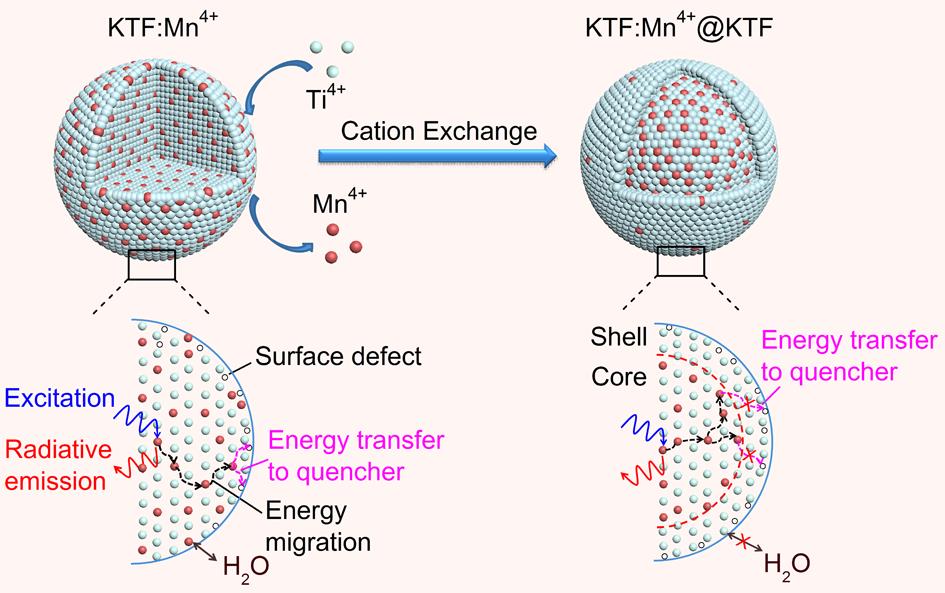
The construction of KTF:Mn4+@KTF core-shell phosphor through a reverse cation exchange strategy and the PL quenching processes.(Image by Prof. ZHU’s Group)
Contact:
Prof. ZHU Haomiao
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: zhm@fjirsm.ac.cn