3–5 μm mid-infrared ( mid-IR) lasers have important applications in photoelectric areas, laser medicine, optical parametric oscillation pumping etc. Previous studies have paid considerable efforts on exploring the nonlinear optical (NLO) materials used in the mid-infrared fields. AgGaS2 and ZnGeP2 are typical commercialized IR NLO materials. However, their low laser damage thresholds (LDTs) dramatically hindered their practical application. Therefore, metal iodates have been considered as potential mid-IR NLO materials due to their excellent characters.
mid-IR) lasers have important applications in photoelectric areas, laser medicine, optical parametric oscillation pumping etc. Previous studies have paid considerable efforts on exploring the nonlinear optical (NLO) materials used in the mid-infrared fields. AgGaS2 and ZnGeP2 are typical commercialized IR NLO materials. However, their low laser damage thresholds (LDTs) dramatically hindered their practical application. Therefore, metal iodates have been considered as potential mid-IR NLO materials due to their excellent characters.
In a recent study published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., a research group led by Prof. YE Ning from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter (FJIRSM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed the first ammonium-containing metal iodate fluoride, 


 (NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5, by introducing F- anions and NH4+ anionic groups into bismuth-containing iodates, and the new NLO material achieved great performances.
(NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5, by introducing F- anions and NH4+ anionic groups into bismuth-containing iodates, and the new NLO material achieved great performances.
The researchers found that (NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5 showed a very strong second harmonic generation(SHG) response (9.2 ′ KH2PO4), suitable birefringence (Δn = 0.0690 at 589.3 nm), and high LDT(40.2′AgGaS2).
The 


 bismuth-containing iodates usually possess high probabilities to achieve large SHG responses due to the potentiation of polarizable lone-pair electrons in Bi3+ as well as IO3- anionic groups. The superposition of polarization in (NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5 was beneficial to the dipole moment, which further enhanced the SHG response of (NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5.
bismuth-containing iodates usually possess high probabilities to achieve large SHG responses due to the potentiation of polarizable lone-pair electrons in Bi3+ as well as IO3- anionic groups. The superposition of polarization in (NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5 was beneficial to the dipole moment, which further enhanced the SHG response of (NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5.
The researchers introduced fluoride anions into the bismuth-containing iodates in order to enlarge the bandgap and further increase the laser damage threshold. (NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5 exhibited a high LDT value (40.2′AgGaS2).
Moreover, the researchers revealed that the  introduction of NH4+ anionic groups can not only reinforce the bonding interaction between
introduction of NH4+ anionic groups can not only reinforce the bonding interaction between  [Bi2(IO3)2F5]- layers, but also reduce the growth temperature. H atoms in NH4+ anionic groups can form N-H···F hydrogen bonds with F anions in [Bi2(IO3)2F5]- layers. The growth temperature of (NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5 is 160 °C, which is lower than growth temperatures of most bismuth-containing iodates.
[Bi2(IO3)2F5]- layers, but also reduce the growth temperature. H atoms in NH4+ anionic groups can form N-H···F hydrogen bonds with F anions in [Bi2(IO3)2F5]- layers. The growth temperature of (NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5 is 160 °C, which is lower than growth temperatures of most bismuth-containing iodates.
This study provides an effective way to explore and design mid-IR NLO materials with strong SHG responses and large LDTs.
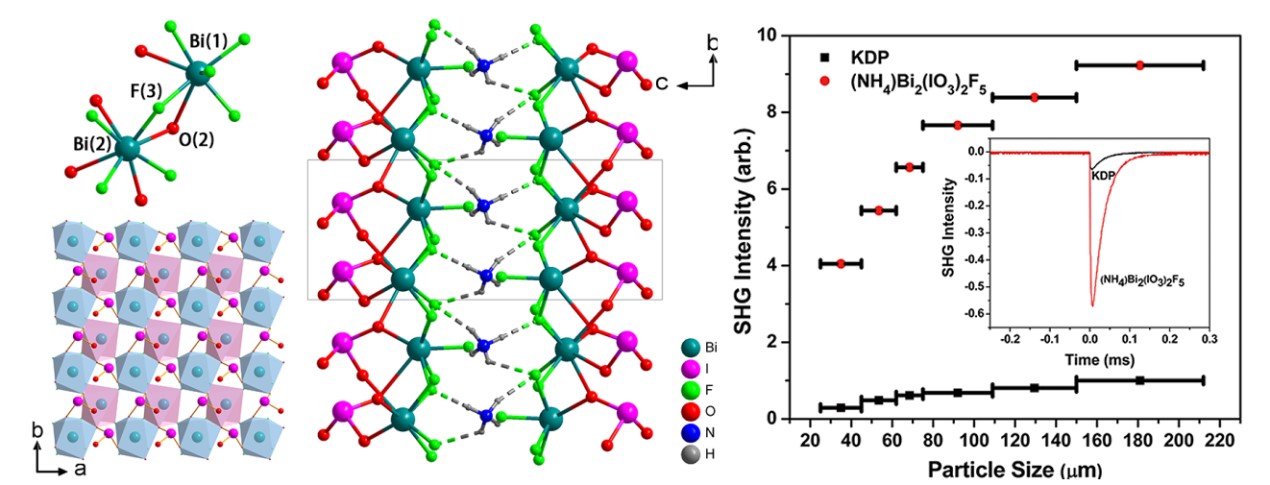
Illustration of structural of (NH4)Bi2(IO3)2F5 and the strong SHG response (Image by Prof. YE’s group)
Contact:
Prof. YE Ning
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
E-mail: nye@fjirsm.ac.cn