Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) is a promising solution for improving spectrum efficiency, user fairness and total throughput in visible light communication (VLC) systems. However, the transmission performance of the NOMA-VLC system is largely limited by error propagation problems, linear and nonlinear distortion caused by multipath, limited modulation bandwidth, and the nonlinearity of light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
In a study published in Journal of Lightwave Technology, the research group led by Prof. LIN Bangjiang from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter (FJIRSM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported a machine learning based signal demodulator in NOMA-VLC.
The researchers proposed a NOMA-VLC demodulator based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to jointly realize signal compensation and recovery. To this end, they conducted simulation and experimental studies to prove the feasibility of the CNN-based Rx proposed in NOMA-VLC.
They established the LED nonlinear model to make the NOMA signal at the transmitter suffer nonlinear damage in the simulation part. And in the experimental part, they verified the advantages of the CNN demodulator by adjusting the input signal amplitude and transmission rate of the optical link.
Simulation and experiment results show that the proposed CNN-based demodulator can effectively compensate linear and non-linear distortions induced by multipath dispersion, limited modulation bandwidth and nonlinearity of LEDs, thereby achieving higher bit error rate performance compared with receivers based on successive interference cancellation (SIC) and joint detection (JD).
It can be seen that compared with SIC, when the power allocation ratio (PAR) is 0.16, 0.25, and 0.36, the performance gain of User1 is 1.9, 2.7, and 2.7 dB respectively. the performance gain of User2 is 4, 4 and 2.6 dB respectively.
This study provides an effective solution to the problems in NOMA-VLC and contributes to the future development of NOMA-VLC.
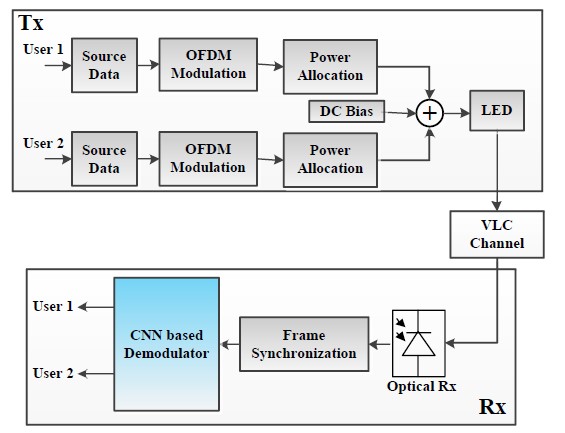
Block diagram of NOMA-VLC system employing a CNN based demodulator.( Image by Prof. LIN’s Group)
Contact:
Prof. LIN Bangjiang
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: linbangjiang@fjirsm.ac.cn