Oriented metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) films are attracting great attention due to their fascinating physicochemical properties and unique functionalities. Since Stoddart, Yaghi, and coworkers reported the first series of CD-MOFs from γ-cyclodextrin and alkali metal salts in 2010, CD-MOFs, particularly γCD-MOFs constructed from γ-cyclodextrin (γCD) and K2CO3, have emerged as a kind of homochiral, edible, and porous materials.
Such crystalline, supramolecular CD arrangements exhibit rich host-guest chemistry and the straightforward fabrication of such compounds triggered a large amount of research on the applications for adsorption/separation, proton conductivities, purification of petrochemicals, drug delivery, electrical memristors, and biomedicine. Particularly, peptides as a kind of biomolecules are constructed from two or more amino acids, which serve as potential high-value and broadly applicable compounds in drugs discovery.
In a study published in CCS Chem., Prof. ZHANG Jian and Prof. GU Zhigang from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the collaborators, reported the surface-oriented assembly of cyclodextrin MOF film for enhanced peptide-enantiomers sensing.
The researchers first unveiled an [110]-oriented biomolecule γ-cyclodextrin (γCD) MOF films with arrayed CD channels running perpendicular to the substrate surface.
They then realized the sophisticated architecture by combining liquid phase eptiaxal layer-by-layer (lbl) methods with a γCD-based thiol self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) functionalized surface.
The porous, nontoxic γCD-SURMOF exhibited a pronounced hydrophilic character, which is beneficial for the recognition and separation of biomolecules. Two model biomolecules, tripeptides of Tyr-(L-Ala)-Phe and Tyr-(D-Ala)-Phe were chosen as probe enantiomers models for a detailed quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation(QCM-D) adsorption study.
Besides, a thorough analysis of the results revealed  that the oriented channels in the γCD-SURMOF lead to a pronounced increase in uptake and diffusion coefficient compared to polycrystalline γCD-MOF films.
that the oriented channels in the γCD-SURMOF lead to a pronounced increase in uptake and diffusion coefficient compared to polycrystalline γCD-MOF films.
This study provides an effective avenue to prepare oriented MOF film with high quality, and a new choice of chiral, nontoxic and porous crystalline network materials for biomolecule recognition and separation applications.
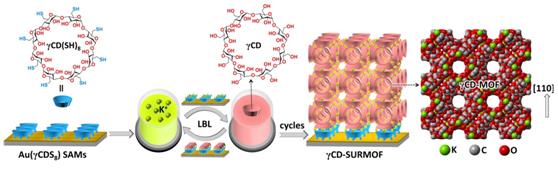
Schematic illustration of the Research (Image by Prof. ZHANG’s group)
Contact:
Prof. GU Zhigang
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter,
Chinese Academy of Sciences
E-mail: zggu@fjirsm.ac.cn