TiO2 has been widely used as a photocatalyst for water splitting due to its high activity, low cost, abundance, safety, and stability. However, the further utilization of TiO2 is still limited to the wide band gap and fast electron recombination speed, so it can only utilize 4% of the energy in the ultraviolet spectral region of the solar spectrum. Therefore, expanding its light absorption range is of great significance.
Carbon is a suitable dopant with metallic conductivity and large electron storage capacity, and the isolated C 2p states can excite high photocatalytic activity under visible light.
In a study published in Appl. Surf. Sci, the research group led by Prof. LU Canzhong from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, reported  the visible light absorption of ultrathin carbon-modified TiO2 nanotube arrays (UTC-doped TiO2@TNT).
the visible light absorption of ultrathin carbon-modified TiO2 nanotube arrays (UTC-doped TiO2@TNT).
The researchers prepared TiO2 nanotube arrays by electrochemical anodic oxidation method, using a trace amount of ethylene glycol in the electrolyte as the carbon source. They prepared the ultra-thin carbon-modified TiO2 nanotube arrays by an ultra-thin ethylene glycol adsorption and vacuum annealing treatment, which is simple and efficient and requires no additional carbon source.
The linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) curves showed that there is a peak photocurrent density (0.6 mA×cm-2) with a max photoelectric-conversion efficiency (η=0.4%) for the UTC-doped TiO2@TNT under visible light irradiation, which is significantly improved compared to ordinary TiO2 materials in the visible region.
They also evaluated the light absorption range of UTC-doped TiO2@TNT using an incident photo-to-current efficiency (IPCE) test. The results show that UTC-doped TiO2@TNT still has photocurrent at a wavelength of 600 nm, indicating that its photoabsorption range extends to 600 nm.
Thanks to the induced doping energy level of ultrathin carbon, the UTC-doped TiO2@TNT photocatalyst can absorb both ultraviolet(UV) and visible light. In addition, carbon has metallic conductivity and a large electron storage capacity. Therefore, carbon atoms can trap photo-generated electrons on the surface of TNT, effectively enhancing the separation of photo-generated charge carriers.
This study shows that introducing ultrathin carbon can effectively reduce the band gap of TiO2 and extend the TiO2 light absorption to the visible region.
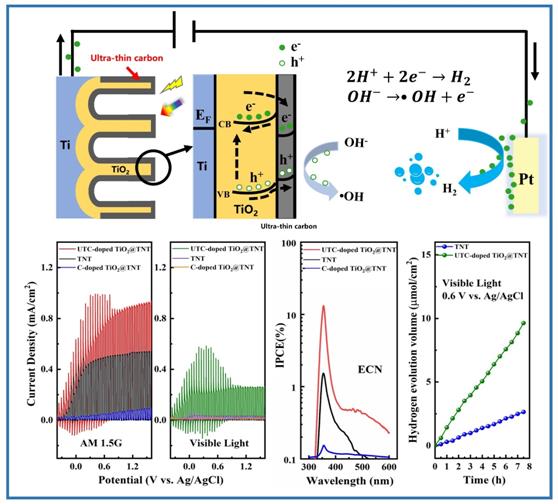
Illustration of the Research (Image by Prof. LU’s group)
Contact:
Prof. LU Canzhong
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: czlu@fjirsm.ac.cn