Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) are widely used in high-end equipment manufacturing, and model-free predictive control (MFPC) is applied to essentially enhance robustness.
However, the MFPC strategy based on ultra-local cannot fully meet the requirements due to limited model accuracy and objective quality. As the third generation of advanced control technology in the motor driving realm, further exploring its potential is necessary to achieve excellent control performance. Adjusting the data-driven model structure to improve model accuracy and implementing it under continuous-control-set (CCS) condition is an effective way to meet harsh requirements.
In a study published in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, Prof. WANG Fengxiang’s group from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter of the Chinese Academy of Sciences designed a novel MFPC strategy using time-series subspace in a PMSM driving system. This method skillfully avoids the difficulty of matrix inverting and partial derivative calculations under CCS condition, to address the issue of hard realization of the time-series subspace model, and achieve better model and control accuracies.
Due to the mechanical compositions in the motor, the changing rate of electrical variables becomes slower due to the inertial term, and these variables satisfy the time-series characteristic. The researchers adjusted the input and output signals and designed a time-series subspace model in MFPC with a group of discrete-time transfer functions in reverse, considering the time-series characteristics, to clarify the meaning of signals.
Two vectors are grouped relating to the sampled data and model coefficients respectively. A recursive least squares (RLS) algorithm is adopted to online estimate the coefficients in the model within each sampling period, and maintain the accuracy of the model to clearly reflect the current operating state of the plant. Due to the small enough sampling period, a time-shift consideration is applied to generate the future output signal, where the future input signal is replaced by its future reference tuned by the Lagrange algorithm since it wishes to reach the reference value at the next sampling period.
The researcher deeply analyzes the locations of system poles and zeros, to determine the stability under the conditions of parameter mismatches. The poles’ locations for the model-based predictive control (MBPC) have obvious moving distances toward to the imaginary axis, and some conjugate poles enter into the unstable range if the mismatch degree increases continuously. Compared to MBPC, the poles from the proposed method have almost the same location with enough gains, which is not affected by parameter mismatches.
A current control system for a PMSM driving system is selected as an example to demonstrate the correctness of the presented method. According to experimental results, compared to the conventional MFPC based on ultra-local under the same operating conditions, the proposed method obtains improved current sine degree, model quality, and system noises, and the robustness is effectively enhanced.
In addition, the proposed method exhibits sufficient compatibility to be applied to other motor drive systems or power electronics topologies to achieve improved control performance.
This study provides valuable guidance for the future design and development of MFPC strategies that require high-quality predictive accuracy for motor drives.
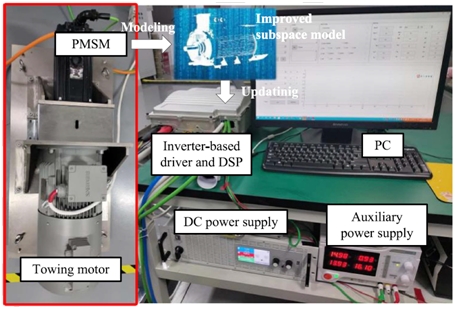
Illustration of the Research(Image by Prof. WANG’s group)
Contact:
Prof. WANG Fengxiang
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: fengxiang.wang@fjirsm.ac.cn