Facile-synthesis and low-cost X-ray scintillators with high light yield, low detection limit and high X-ray imaging resolution have many important applications in medical and industrial imaging fields. However, the optimal balance between X-ray absorption, decay lifetime and excitonic utilization efficiency of scintillators for achieving high-resolution imaging is hard to realize.
In a study published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., the research group led by Prof. ZHENG Fakun and Prof. GUO Guocong from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter of the Chinese Academy of Sciences designed thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF)-active coinage-metal sulfide clusters scintillators.
The researchers synthesized two thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF)-actived coinage-metal clusters M6S6L6 (M = Ag or Cu) by simple solvothermal reaction, where the cooperation of heavy atom-rich character and TADF mechanism supports strong X-ray absorption and rapid luminescent collection of excitons.
They found that TADF materials with small singlet-triplet energy difference (DEST) offer an opportunity for reversed intersystem crossing (RISC) of triplet excitons to the singlet state at the thermal actuation, and play a unique role in concurrently improving exciton emission efficiency and rapid radiative decay. Metal clusters system, featuring the rich heavy atoms, is the preferred choice to increase the X-ray absorption.
Besides, the researchers revealed that SC-Ag displays a high photoluminescence quantum yield of 91.6% and scintillating light yield of 17420 photons MeV–1, as well as a low detection limit of 208.65 nGy s–1 that is 26 times lower than the medical standard (5.5 mGy s–1).
Theoretical calculation and experimental results revealed that metal coordinating donor-acceptor (D-A) conformation organic motif modulates orbital distributions, and induces highest-occupied-molecular-orbital (HOMO) and lowest-unoccupied-molecular orbital (LUMO) orbital separation and small DEST, which is the main reason for TADF emission of coin metal clusters.
Moreover, the researchers applied scintillating screen comprised of SC-Ag in the X-ray imaging system and a high imaging resolution of 16 lp/mm was demonstrated .
This study is the first exploration of hexanuclear silver cluster in X-ray imaging. It provides a promising approach to design scintillators with excellent performance, and offers more possible choices for scintillator system.
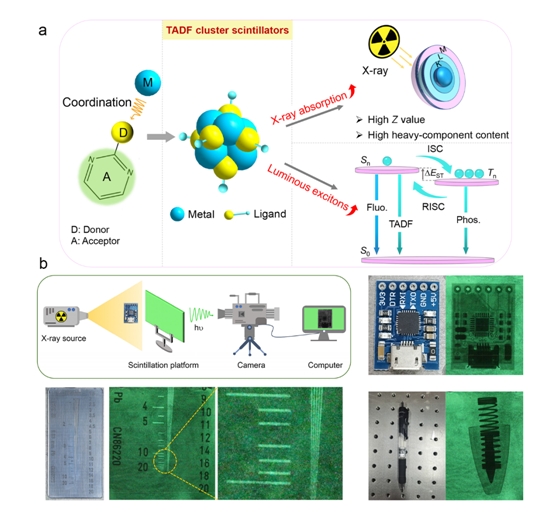
Illustration of the Research (Image by Prof. GUO’s group)
Contact:
Prof. GUO Guocong
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: gcguo@fjirsm.ac.cn