Atherosclerosis (AS) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, seriously threatening human health. The diagnosis and treatment of AS has become one of the research hotspots as scientists want to reduce the incidence of sudden cardiovascular disease caused by AS.
The development of early diagnostic techniques for AS plaques still has challenges in the medical field. Many diagnostic techniques have been reported for the detection of AS plaques, but only at a later stage of plaque development, and few studies have been reported on imaging at the early stage of AS formation.
In a study published in ACS Nano, the research group led by Prof. ZHANG Yun at the Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, fabricated a foam cell-targeting nanoprobe based on near-infrared persistent luminescent nanoparticles (NIR PLNPs) to achieve highly sensitive detection of early AS plaques by persistent luminescence (PersL) imaging.
The researchers synthesized a NIR PLNP (mZGS) by mesoporous silica (mSiO2) templating method and prepared a nanotargeting probe (mZGS-OPN) by modifying the surface of the nanoparticle with maleimide-polyethylene glycol-active ester (MAL-PEG5000-NHS) and an anti-osteopontin (OPN) antibody. The nanoprobe was homogeneous in shape and size, with excellent PersL properties and active targeting.
In vitro cellular experiments demonstrated that mZGS-OPN was able to specifically bind to the highly expressed OPN on the surface of foam cells, offering the possibility of realizing the detection of AS plaques. Using AS model mice, the researchers confirmed the gradual increase of AS plaques and the presence of highly expressed OPN in the plaques as the model time progressed.
In addition, they intravenously injected mZGS-OPN into AS model mice and found that the nanoprobe was able to achieve imaging detection of AS plaques by actively targeting aggregation in AS plaques. Notably, mZGS-OPN achieved 2-week imaging of tiny plaques using highly sensitive PersL imaging, earlier than MRI and US imaging.
This study is the first PersL-based imaging for the detection of AS, and is a breakthrough in the diagnostic study of early microplaques.
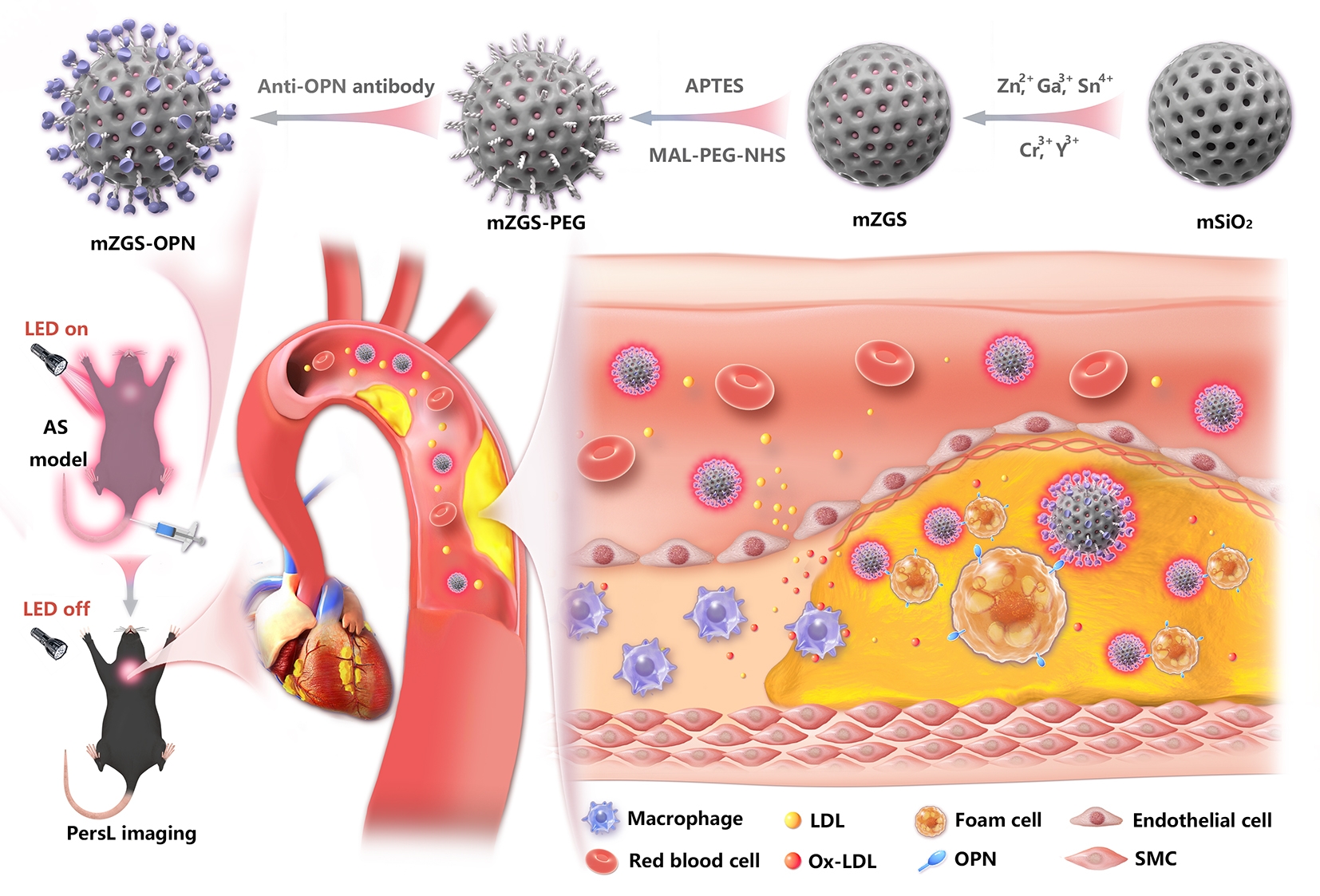
Near-infrared persistent nanoprobe for early AS plaque imaging (Image by Prof. ZHANG Yun's group)
Contact:
Prof. ZHANG Yun
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: zhangy@fjirsm.ac.cn