In the field of nonlinear optics (NLO), deep ultraviolet (DUV) NLO crystals have garnered significant attention due to their crucial role in all-solid-state lasers. With ongoing research, the demand for these DUV NLO crystals continues to grow.
Currently, DUV NLO crystals that simultaneously exhibit a large optical band gap and strong second harmonic generation (SHG) response are mainly found in carbonates, borates, and nitrates containing π-conjugated elements.
In contrast, sulfates and phosphates, without π-conjugated functions, typically struggle to achieve similar performance due to their smaller microscopic second-order polarizability. Most DUV NLO phosphates have SHG responses that struggle to surpass the performance limit of 3 × KDP.
In a study published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, a research group led by Prof. ZHU Qilong and Prof. LIN Hua from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a "polar-axial-symmetry screening" strategy for this challenge.
Researchers discovered a magnesium-based phosphate compound, Mg2PO4Cl, among more than 10,000 phosphates. This compound exhibits the highest SHG response (5.2 × KDP) among DUV NLO crystals containing non-π-conjugated elements, with a cutoff edge estimated at 179 nm and a birefringence of 0.046@1064 nm according to hybrid functional calculations.
First-principles calculations indicated that the excellent NLO performance of Mg2PO4Cl primarily arises from the effective stacking of three functional motifs, [PO4], [MgO5Cl], and [MgO4Cl2], along the polar axis [001], where non-bonding electrons of O-2p and Cl-3p are preferentially aligned in the same direction.
Berry phase analysis revealed the role of the hybridization degree of P–O bonds in enhancing the SHG response. Moreover, a detailed analysis and comparison of the structure-property relationships of other advanced DUV NLO compounds containing non-π-conjugated elements further validate the effectiveness of this polar-axial-symmetry screening strategy.
These research findings not only demonstrate the immense potential of phosphate compounds in the DUV NLO crystal field but also provide new insights for future crystal design. The proposed polar-axial-symmetry screening strategy will help deepen the understanding of structure-property relationships and promote the development of NLO crystal materials.
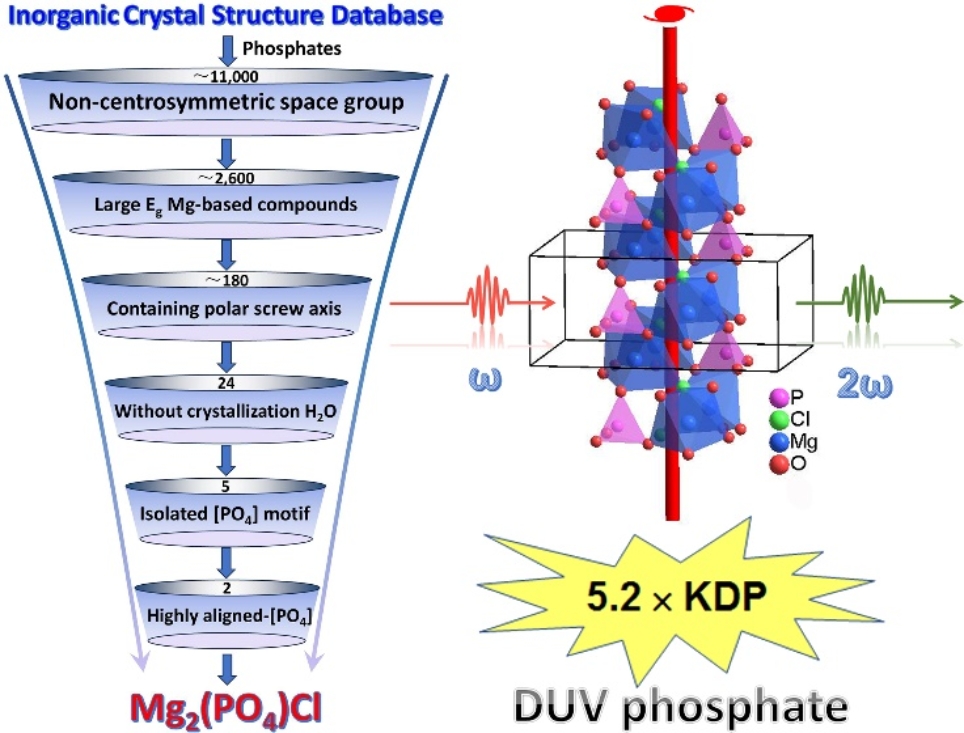
Illustration of the Research (Image by Prof. ZHU’s group)
Contact:
Prof. ZHU Qilong
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: qlzhu@fjirsm.ac.cn