Ultraviolet nonlinear optical (UV NLO) crystals are pivotal for converting the wavelength of solid-state lasers into the short-wave ultraviolet region, with applications in medical technology, industrial processing, military, and scientific research. An ideal UV NLO crystal should possess a large second-harmonic generation (SHG) response (> 0.39 pm/V), appropriate birefringence (0.05-0.10 @1064 nm), and a short cutoff edge. Traditional design strategies for UV NLO crystals rely on conventional planar π-conjugated groups (e.g., BO33-, CO32-, NO3-, C3N3O33-, etc.), requiring extensive experimentation and iterative trial-and-error to achieve desired structures. Consequently, the rational design and efficient synthesis of UV NLO crystals with balanced performance remain a significant challenge, necessitating the development of effective strategies.
In a recent study published in Angewandte Chemie, Prof. LUO Min's research group from the Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, proposed a novel approach to efficiently synthesize UV NLO crystals with balanced performance. The integration of Secondary Building Unit (SBU) design with crystal engineering is expected to open a new avenue for crystal structure design.
Crystal engineering serves as a robust approach to designing and synthesizing new compounds with targeted structures and functions by substituting functional modules in parent materials. However, traditional substitutions have been limited to conventional group exchanges, restricting performance optimization. To address this, Prof. Luo’s team pioneered a strategy of constructing novel SBUs with balanced microscopic properties to overcome the inherent limitations of simple functional groups,and subsequently applied crystal engineering to replace functional modules in parent materials with SBUs.
Using β-BaB2O4 (β-BBO) as a template—a crystal with strong SHG but excessive birefringence. Based on the C3-symmetric structure of the B3O63- unit in β-BBO and engineered to deliver balanced NLO properties, Pro. Luo's team innovatively designed the C3-symmetric SBU [Be3(OH)3(COO-CH2-COO)3]3−. In the new SBU, multiple bidentate chelation of the π-conjugated C3H2O42- groups ensures high hyperpolarizability, while the orthogonal alignment of these groups relative to the Be3(OH)33+ plane optimizes polarizability anisotropy. Ultimately, through crystal engineering, Luo’s team successfully replaced B3O63- in β-BBO with this new SBU and Ba2+ with Li+, obtaining a new β-BBO-liked compound, Li3[Be3(OH)3(C3H2O4)3]·7H2O (LBOC), which crystallizes in the same R3c space group as β-BBO.
LBOC was grown via an aqueous solution method, yielding centimeter-sized single crystals. Characterization confirmed that LBOC exhibits a short UV cutoff edge (200 nm), a large SHG (4 × KDP), and a suitable birefringence (0.067 @ 589.3 nm). These well-balanced properties position LBOC as a promising UV NLO crystal. Moreover, the successful SBU substitution offers a novel strategy for rationally controlling both structure and performance in NLO materials.
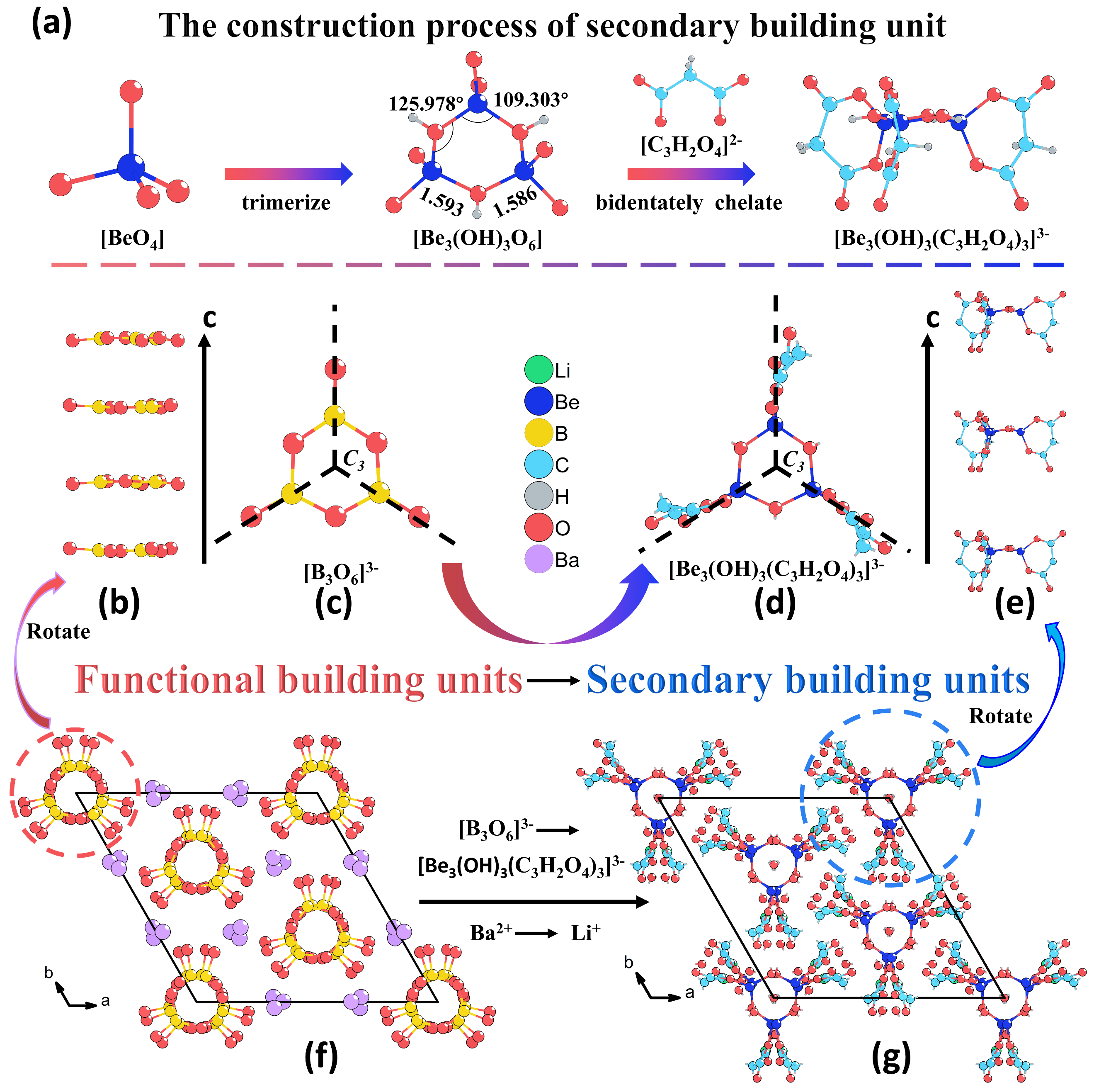
(a) The construction process of second building unit; A sequence of B3O63- groups in β-BBO (b) and SBUs in LBOC (e) stacked along the c direction; Comparison of B3O63- unit (c) and SBU (d); Structure of β-BBO (f) and LBOC (g). (Image by Prof. LUO’s group)
Contact:
Prof. LUO Min
Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: lm8901@fjirsm.ac.cn